The Presence of the Running Machine on the Internet
Everything has a start, and has an end.
Deploying a server over the Internet is different from setting up a local server without being revealed to outside people. For a server to be unknown on the Internet by fully-qualified hostname, it requires some registration processes. Furthermore, since the server is known to the public, some security measures should have been taken to avoid the abuse of the server.
This package includes basic elements for network operation, for example, DNS, FTP, firewall, backup storage server, VPN (Virtual Private Network) and Email .
We start from the introduction on Domain name registration with the following diagram:
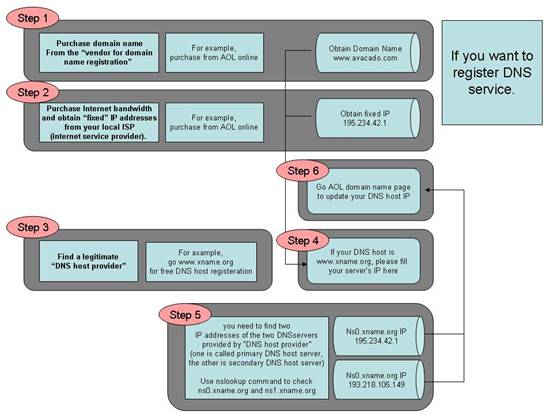
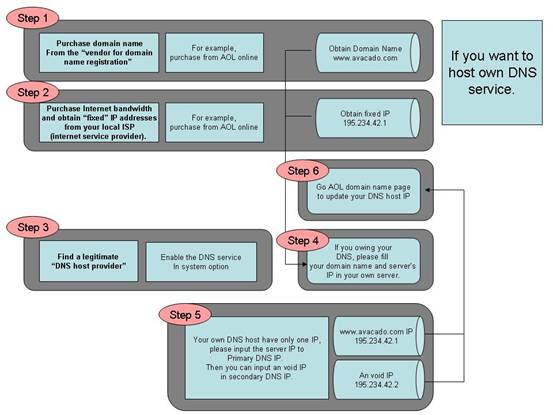
1. Purchase domain name from the “vendor for domain name registration”
The “Domain Name Registration Vendor” usually will provide a Web interface for you to query your desired domain name. You may find some of the domain names you like have been acquired by other people. It is necessary for you need to find a domain name that is not being occupied. And then make the purchase of the domain name from the “Domain Name Registration Vendor” to complete this step.
2. Purchase Internet bandwidth and obtain “static” IP addresses from your local ISP (internet service provider).
Usually, the ISP will give you a set of IP addresses that may include a list of public IP addresses, the netmask, and the default Gateway. This IP information will be used when you install the software and configure your server. You shall keep the information in a safe place once you obtain that from your ISP.
3. Find a legitimate “DNS host provider”
It is to host your domain name (which you get from step 2) and the associated static IP address (which you get from step 3) record so that everybody on Internet can use your domain name to reach your server. Usually, the “DNS host provider” will provide a Web interface to allow you to input your domain name and the mapped IP address record into their hosted server. This step is completed after you have entered the data into the web page.
4. Update the record at the “Domain Name Registration Vendor” server with the IP addresses of the “DNS host provider”.
At this step, you need to access the website provided by “Domain Name Registration Vendor”. If you do not know the DNS server’s IP addresses of your “DNS host provider”, you can do as follows at your Windows command prompt (the command prompt is reached through Start > Run > cmd), issue the command
C:\>nslookup DNS-server- name-from-your-provider
The system will respond with the IP address of your “DNS host provider”. Usually, you need to find two IP addresses of the two DNS servers provided by “DNS host provider” (one is called primary DNS host server, the other is secondary DNS host server). The two IP addresses will be entered into the record in the place of “Domain Name Registration Vendor”. We suggest using primary DNS server and secondary server from different places. The Azblink server package also provides DNS server. But to allow people all over the world can query your domain, you should have your domain name placed in different DNS servers to alleviate the load.
5. Wait until it is in effect.
In general, it needs 24 hours to 72 hours to have your domain name record of the server populated across the world so that people can use domain name to access your server.
Those are the general steps as long as you want to have your own private server(s) on Internet. |